NAAC Binary Accreditation Explained: A New Era in Higher Education
By, Kramah Team

In 2024, the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) introduced a major shift in how higher education institutions in India are evaluated. The NAAC Binary Accreditation system replaces the old CGPA-based grades with a simple status: Accredited or Not Accredited.
The new system makes accreditation easier to understand, more transparent, and fairer for institutions. It also sets a foundation for continuous improvement through the Maturity-Based Graded Level (MBGL).
What Is NAAC Binary Accreditation?
The NAAC Binary Accreditation system is a standard shift from the earlier CGPA-based grading system. Under this new framework:
- Institutions are assessed based on their compliance with specific criteria.
- Each criterion is evaluated as either “Yes” (compliant) or “No” (non-compliant).
- The final accreditation status is determined by the number of “Yes” responses across all criteria.
This approach ensures a more objective and transparent evaluation process, reducing subjectivity and promoting accountability.
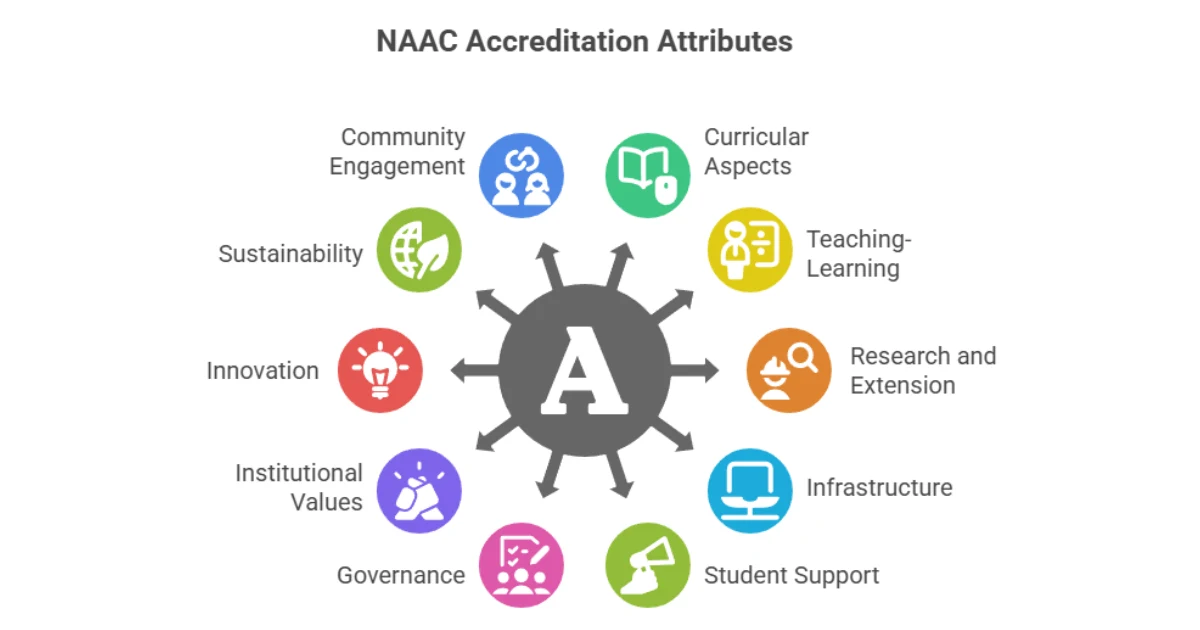
The 10 Key Attributes of NAAC Binary Accreditation
Under the new framework, institutions are evaluated based on 10 key attributes, which encompass various aspects of institutional functioning. These attributes serve as the foundation for the accreditation process:
- NAAC Attribute 1: Curricular Aspects
- NAAC Attribute 2: Teaching-Learning and Evaluation
- NAAC Attribute 3: Research and Extension
- NAAC Attribute 4: Infrastructure and Learning Resources
- NAAC Attribute 5: Student Support and Progression
- NAAC Attribute 6: Governance, Leadership, and Management
- NAAC Attribute 7: Institutional Values and Best Practices
- NAAC Attribute 8: Innovation and Best Practices
- NAAC Attribute 9: Sustainability and Environmental Impact
- NAAC Attribute 10: Community Engagement and Outreach
Each attribute comprises specific criteria that institutions must meet to achieve accreditation.
Maturity-Based Graded Level (MBGL)
Following the binary accreditation, institutions have the opportunity to apply for the Maturity-Based Graded Level (MBGL), which assesses the maturity of institutions across various parameters.
The MBGL places colleges and universities into five clear levels of maturity:
Level 1: Basic – The institution meets the minimum standards but has room to improve in most areas.
Level 2: Developing – The institution shows progress and has started to strengthen its systems and processes.
Level 3: Established – The institution has stable practices, strong academic performance, and consistent outcomes.
Level 4: Advanced – The institution demonstrates innovation, leadership in higher education, and strong national presence.
Level 5: Institutions of Global Excellence – The highest recognition, given to institutions that perform at international standards with global impact.
This framework helps institutions showcase their progress over time, giving stakeholders—students, parents, and policymakers—a clear picture of where the institution stands today and where it is headed.
Key Features of the Binary Accreditation System
- Simplified Evaluation: The binary system eliminates the complexities associated with CGPA grading, making the accreditation process more straightforward for both institutions and evaluators.
- Objective Assessment: By focusing on compliance with specific criteria, the system ensures a more objective evaluation, minimizing biases and inconsistencies.
- Enhanced Transparency: The clear “Yes” or “No” responses for each criterion provide institutions with a transparent understanding of their strengths and areas for improvement.
- Encourages Continuous Improvement: Institutions are motivated to continuously enhance their practices to achieve and maintain accreditation status.
Comparison With the Old NAAC Framework
| Aspect | Old CGPA System | NAAC Binary Accreditation |
|---|---|---|
| Grading | A++ to D (CGPA) | Accredited / Not Accredited |
| Metrics | 7 criteria | 10 Criteria |
| Evaluation | Subjective, weighted | Objective, Yes/No based |
| Reporting | Manual spreadsheets | Automated digital reports |
| Audit | Field visits required | AI-assisted possible |
| Preparation | Annual | Continuous compliance monitoring |
Read detailed Comparison of NAAC New Binary Accreditation System vs NAAC old CGPA-Based Grading System Here
Changes Colleges Must Adapt To
The transition to binary accreditation requires institutions to rethink their approach:
- Full Documentation Readiness: Every metric must have verifiable evidence. Missing documentation can result in a “No.”
- Continuous Monitoring: Accreditation is now a year-round activity, not just an annual exercise.
- Outcome-Based Assessment: Focus on student outcomes, research outputs, and institutional performance.
- Digital Submissions & AI Checks: NAAC may use AI-assisted inspections to verify online submissions.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Faculty, staff, and students need to be actively involved in compliance and reporting.
These adaptations are critical to ensure Accredited status and long-term institutional growth.
Key Features of Kramah KI-NAAC Software for NAAC Binary Accreditation
Technology plays a pivotal role in simplifying compliance. Kramah Software helps institutions:
- Automated Mapping: Documents are mapped directly to the 10 key attributes.
- Dashboards & Alerts: Real-time tracking of compliance and pending tasks.
- One-Time Data Entry: Upload once and use across AQAR, SSR, and Binary reports.
- Audit-Ready Repository: Version control, secure storage, and complete audit trails.
- Cross-Framework Support: Aligns with NAAC, NBA, NIRF, and OBE reporting requirements.
- Faculty & Staff Notifications: Automatic reminders for deadlines and updates.
Institutions using Kramah report up to 40% faster submission times and fewer missing metrics errors (Higher Education Technology Survey, 2024).
Summary
The NAAC Binary Accreditation system (2024) replaces CGPA grades with a simple Accredited/Not Accredited status. It introduces 10 key attributes, objective assessments, and digital workflows. Institutions must adapt to stricter compliance, evidence-based evaluation, and continuous improvement. MBGL offers further classification into five maturity levels.
Conclusion
The NAAC Binary Accreditation system represents a significant step towards enhancing the quality and transparency of higher education in India. By focusing on compliance with specific criteria and embracing digital tools, institutions can navigate this new framework effectively and continue their journey towards excellence.
For more detailed information, institutions can refer to the official NAAC documents and guidelines available on the NAAC website.
👉 Book a demo with Kramah Software today to ensure your institution is fully prepared for NAAC binary accreditation in 2025.
FAQ's:
(Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the new NAAC binary system?
The binary system replaces grades like A++, A+, or B with a clear outcome: Accredited or Not Accredited. Each criterion is evaluated as Yes (compliant) or No (non-compliant). The final status depends on the number of “Yes” responses.
What are the changes in NAAC accreditation?
The biggest change is the shift from CGPA grades to a binary system where institutions are marked as Accredited or Not Accredited. The framework also expands from 7 criteria to 10 attributes and introduces digital workflows and the Maturity-Based Graded Level (MBGL) system.
What are the new 10 criteria Of NAAC?
The new framework uses 10 key attributes instead of the earlier 7. These include:
- Curricular Aspects
- Teaching-Learning and Evaluation
- Research and Extension
- Infrastructure and Learning Resources
- Student Support and Progression
- Governance, Leadership, and Management
- Institutional Values and Best Practices
- Innovation and Best Practices
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact
- Community Engagement and Outreach
How does it differ from the old CGPA system?
The old system used cumulative scores (A++ to D). Binary accreditation focuses on objective compliance per metric.
How can colleges prepare?
Centralize data, automate compliance tracking, train staff, and monitor gaps continuously.
Is this system aligned with NEP 2020?
Yes, binary accreditation aligns with NEP 2020 goals of transparency, accountability, and quality.
Can Kramah's Ki-NAAC software help?
Yes. Kramah NAAC software automates mapping, dashboards, and report generation.